|
|
Details of Our Technologies
Dissolving Micropiles
By combining the microfabrication technology in the semiconductor technology
and biotechnology, Professor Takada, Kyoto Pharmaceutical University, has
made it possible to make microparticles individually, one by one. BioSerenTach
(BT) is now developing “Dissolving Micropile Chip” that gives a solution
to pharmaceutical industries, poor bioavailability problem of API.
Dissolving micropile (DM) is a transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS)
and is applicable to the drugs of which clinical dose is less than several mg
like peptide, protein, vaccine, hormone and organic compound.
Overview of DM
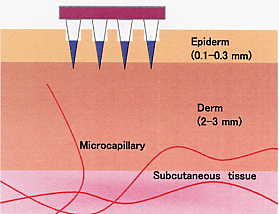
DM has a cone shape and is composed of API and pharmaceutical additives.
DM dissolves rapidly and completely in the epidermis of the skin and can
deliver API into the systemic circulation with high bioavailability. As
its base polymer, thread-forming water soluble polymers such as (1) proteins
like albumin, (2) polysaccharides like chondroitin sulfate, dextran and
hyarulonic acid are used. DM can be prepared under room temperature and
is applicable to peptide/proteins such as recombinant human growth hormone,
erythropoietin, insulin that are degradable by warming. In addition, DM
is applicable to DNA, siRNA and vaccine.
Proof-of-concept experiment
As an example, our study on insulin DM is shown as follows. With a machine, insulin DM chip was prepared and was administered to the rat skin by pressing with fingers and pharmacodynamic study was performed by measuring plasma glucose levels at the insulin dose of 1.73±0.17 IU. As a positive control,
insulin solution was subcutaneously (sc) injected to another group of rats, 1.0
IU/kg. By comparing the total areas above the plasma glucose level vs.
time curve (AAC), relative pharmacological
availability of 52.2% was obtained. BT has developed the second 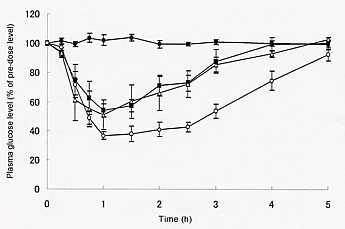

generation DM chip where API is localized at the distal part of microneedles.
100 DMs having 500μm length and 300μm basement diameter were made on a chip, 1.0x1.0cm, as patch preparation. As the distal part of DM, approximately
250-300µm was inserted into the skin, API formulated at the base part of
DM does not contribute the absorption into the skin resulting low bioavailability.
DM containing insulin was evaluated in beagle dogs and the results were
disclosed at #69 annual meeting of American Diabetes Association held in
New Orleans in 2009, June 7-9. Pharmacodynamic (PD) analysis by comparing
the AACs obtained after percutaneous administration of insulin DM chips
and sc injection of insulin solution, relative pharmacological availability
of insulin was determined to be 59.3-71.1%. Pharmacokinetic analysis was
also performed with serum insulin levels vs. time curves and relative bioavailability
(RBA) of 72% was obtained.
Function of DM
(1) Painless administration by percutaneous route
(2) High bioavailability
(3) Applicable to drugs of which clinical dose is less than 1.0mg
(4) High safety (no fear of HIV infection)
(5) Percutaneous delivery of peptide/proteins
(6) Skin vaccine
Other similar technologies
To enhance the skin permeability of drugs, absorption enhancers, iontophoresis,
electroporation and ultrasound have beeb studying. TDDS is severely limited
by the poor permeability of drugs through the human skin, ie most drugs
do not permeate through the skin at therapeutically relevant rates. Microneedles made of metal and polymers like poly(lactic acid) belong to the category of medical
device.
Two-layered DM chip producing machine
Producing machine of DM chips that works under GMP condition is developed
by the fund of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) in 2011.
|
|
Copyright BioSerenTach Inc, 2021
|
|
|

